How Solar Panels Work: Understanding the Science Behind Solar Energy
Solar panels have become a ubiquitous sight on rooftops and in fields, harnessing the power of the sun to generate clean and renewable energy. But have you ever wondered how these panels work? In this blog, we will dive into the science behind solar energy and explain how solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.
The Photovoltaic Effect:
At the heart of solar panels lies the photovoltaic (PV) effect. The term “photovoltaic” comes from the Greek words “photo” meaning light and “voltaic” referring to electricity. PV cells, commonly known as solar cells, are made up of semiconductor materials, most commonly silicon. These materials have properties that allow them to convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Absorption and Electron Excitation:
Solar panels are composed of numerous PV cells connected in series. When sunlight, which is composed of tiny packets of energy called photons, reaches the solar panel, the PV cells absorb the photons. The absorbed photons transfer their energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material of the PV cells.
Electron Flow and Electric Current:
The energy from the absorbed photons causes the electrons in the semiconductor material to become excited and move freely. This movement of electrons creates an electric current within the solar panel. However, the PV cells are designed with specially doped layers to establish an electric field that ensures the electrons flow in a particular direction.
Electricity Conversion:
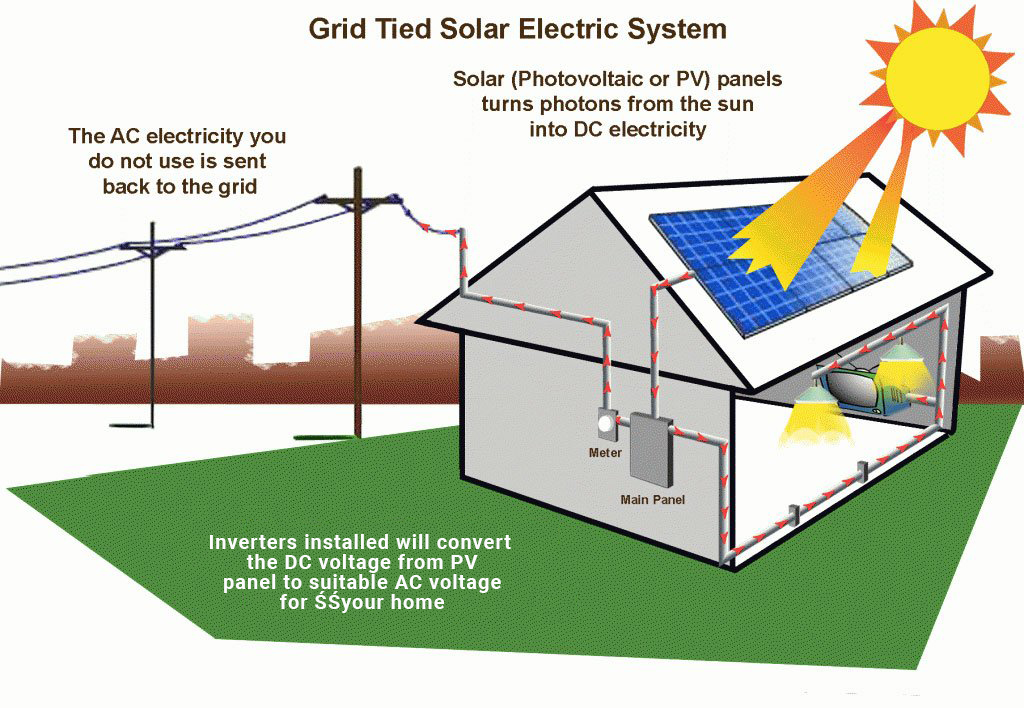
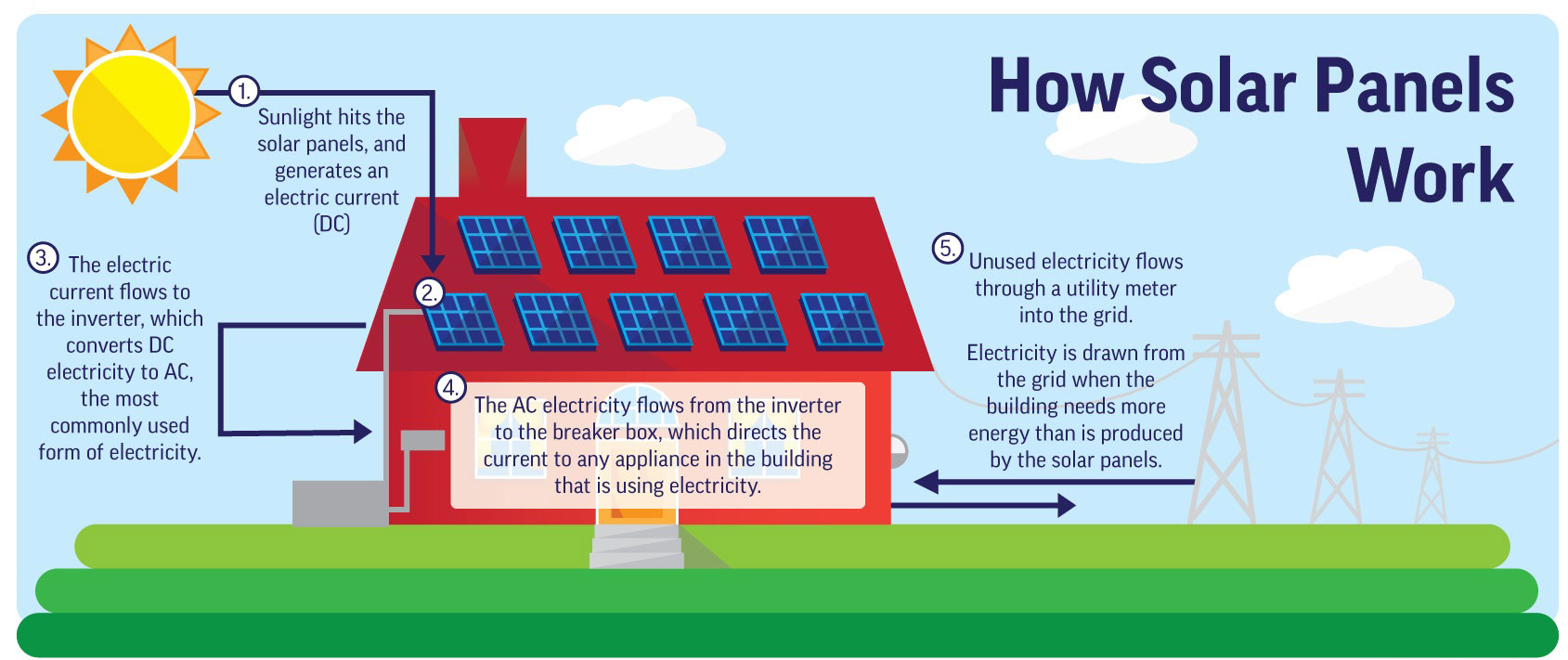
The electric current generated by the PV cells is initially in the form of direct current (DC). However, most of our electrical appliances and the grid operate on alternating current (AC). To make the electricity usable, an inverter is used to convert the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity. This conversion enables the electricity to power homes, businesses, and other electrical devices.
Net Metering and Grid Connection:
Solar panel systems are typically connected to the electrical grid through a process called net metering. When your solar panels produce more electricity than you consume, the excess energy can be fed back into the grid. This allows you to receive credits for the excess electricity, which you can use when your solar panels produce less energy, such as during nighttime or cloudy days. Net metering helps ensure a balanced energy supply and potentially reduces your electricity bills.
Environmental Benefits:
The utilization of solar panels offers numerous environmental benefits. Solar energy is clean and renewable, producing no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. By generating electricity from sunlight, solar panels contribute to reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, combating climate change, and preserving our planet for future generations.
Solar panels are a remarkable technological innovation that converts sunlight into usable electricity. Through the photovoltaic effect, sunlight excites electrons within the PV cells, generating an electric current that can power our homes and businesses. Understanding the science behind solar panels allows us to appreciate the tremendous potential of solar energy in addressing our energy needs sustainably and reducing our environmental impact. As we embrace solar power, we move closer to a cleaner and more sustainable future for all.