The Basics of Solar Energy: A Beginner’s Guide
In an era where renewable energy is gaining significant momentum, solar power stands out as one of the most promising and accessible sources of clean energy. Harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy offers numerous benefits, from reducing carbon emissions to providing energy independence. If you’re new to the concept of solar energy, this beginner’s guide will walk you through the basics and help you understand how solar power works.
How Solar Energy Works:
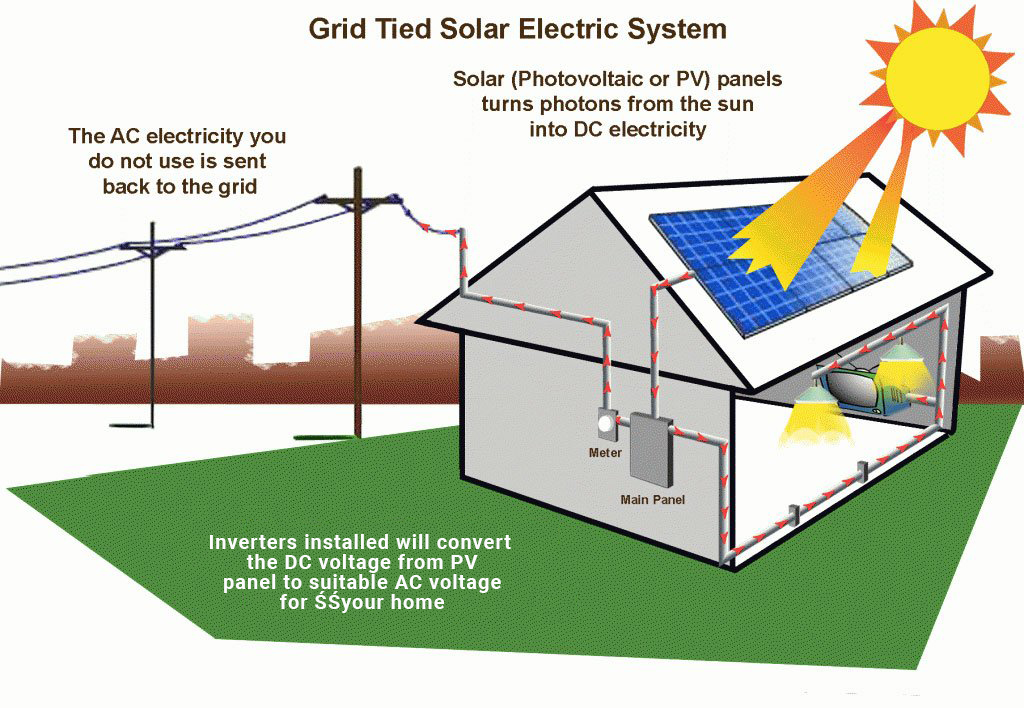
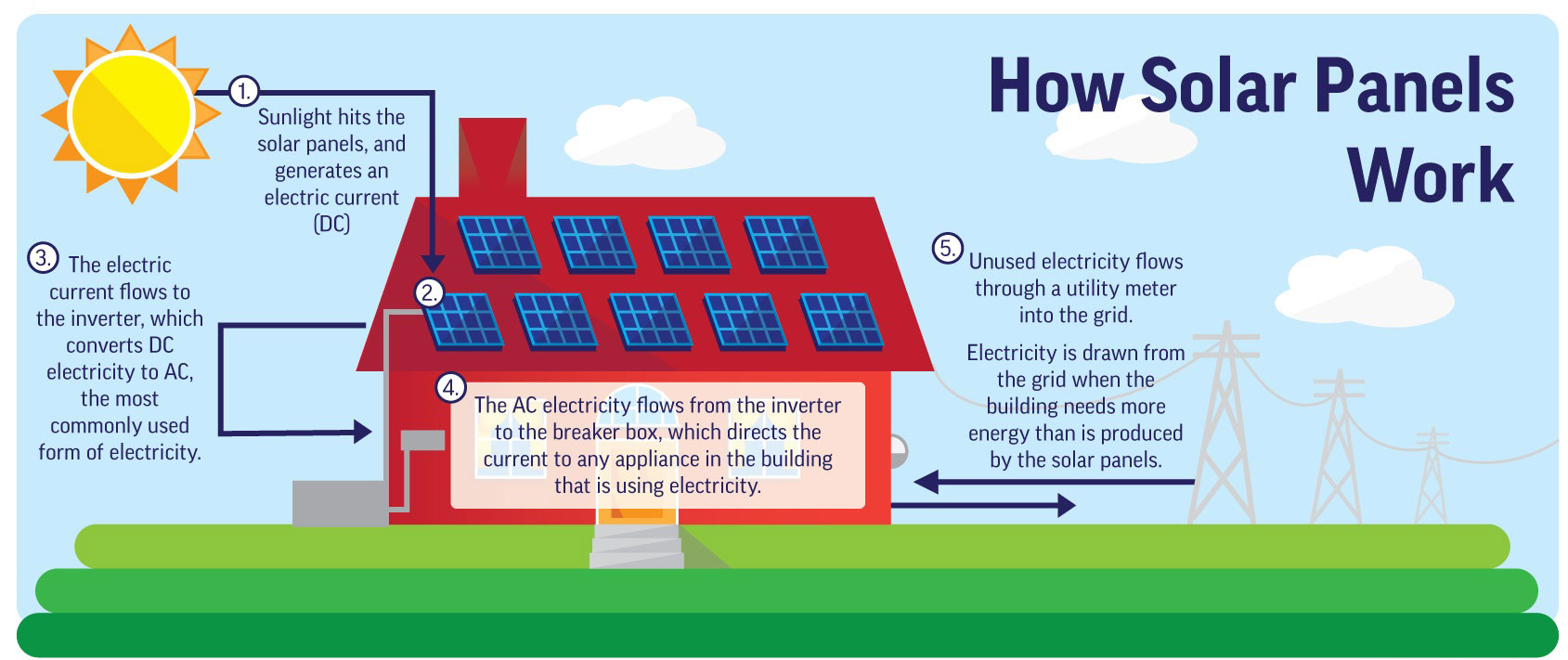
Solar energy is generated through the conversion of sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells, commonly known as solar panels, are made up of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that absorb photons from sunlight. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons excite the electrons in the semiconductor, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) is then converted into alternating current (AC) using an inverter, making it compatible with the electrical grid or for direct use.
Understanding Solar Panels:
Solar panels are the building blocks of a solar energy system. They consist of multiple interconnected PV cells arranged in a panel format. These panels are designed to efficiently capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity. The size and efficiency of solar panels can vary, depending on factors such as the type of solar cells used, the manufacturer, and the available sunlight in a specific location.
Net Metering and Grid Connection:
A significant advantage of solar energy is the ability to connect to the electrical grid through a process called net metering. With net metering, excess electricity generated by your solar panels can be sent back to the grid, and you receive credits for it. During times when your solar panels are not producing enough electricity (such as at night), you can draw electricity from the grid using those credits. This arrangement ensures a seamless and balanced energy supply.
Energy Storage and Battery Systems:
To maximize the benefits of solar energy, many homeowners and businesses are integrating energy storage systems, such as batteries, into their solar power setups. These batteries store excess electricity produced during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or when the grid is down. Energy storage systems offer greater energy independence and the ability to store and utilize solar power at any time.
Environmental and Economic Benefits:
Solar energy offers a range of environmental and economic benefits. By switching to solar power, you significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to combating climate change. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Additionally, solar power can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing dependence on traditional electricity sources, as well as providing protection against rising energy prices.
Solar Energy Applications:
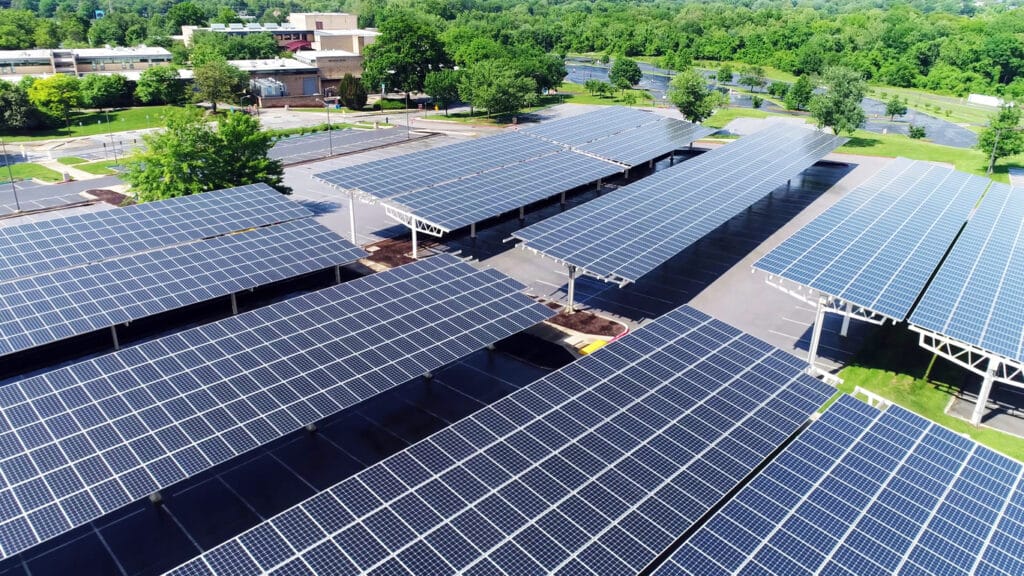
Solar energy can be harnessed for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. In homes, solar panels can power appliances, lighting, and heating systems, resulting in reduced electricity bills. Commercial buildings can benefit from solar power by offsetting operational costs and improving sustainability. Solar energy is also widely used in remote areas or developing regions where access to traditional electricity infrastructure is limited.
As the world transitions towards a sustainable and greener future, solar energy is playing a vital role in meeting our energy needs. Understanding the basics of solar energy empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about adopting solar power solutions. From the science behind solar panels to the environmental and economic advantages, solar energy offers a promising pathway to a cleaner and more sustainable world. Embrace the power of the sun, and together we can create a brighter future for generations to come.